Surface texture parameters provide valuable insights into the characteristics of a surface, helping to evaluate and control surface quality.
AREAL SURFACE TEXTURE PARAMETERS
A long list of parameters
ISO 25178 introduces a standardized nomenclature for surface texture parameters, differentiating them from traditional profile parameters. While profile parameters are prefixed with R (Roughness), W (Waviness), or P (Primary) based on filtering, areal parameters use S (Surface) and V (Volume) prefixes regardless of filtering. This transition to 3D analysis offers a more comprehensive understanding of surface features and behavior.
ISO 25178 introduces a standardized nomenclature for surface texture parameters, differentiating them from traditional profile parameters. While profile parameters are prefixed with R (Roughness), W (Waviness), or P (Primary) based on filtering, areal parameters use S (Surface) and V (Volume) prefixes regardless of filtering. This transition to 3D analysis offers a more comprehensive understanding of surface features and behavior.
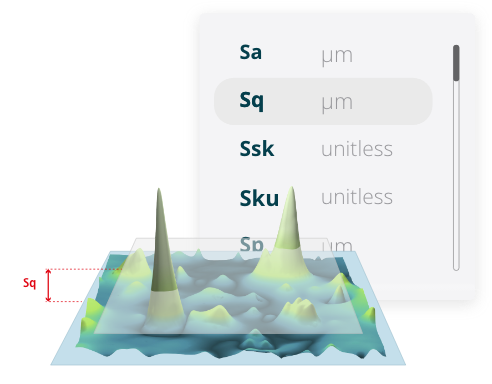
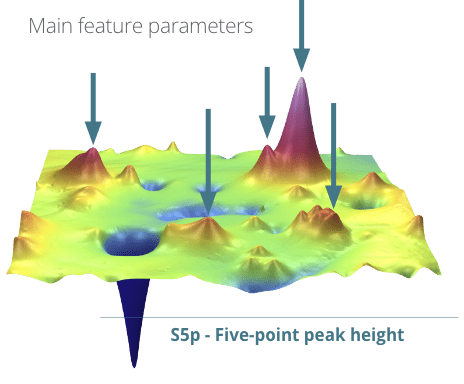
Surface texture parameters can be classified into two groups depending on the dataset used to calculate them: field and feature parameters. While field parameters use all the height datasets, feature parameters only consider specific surface motifs.
Surface texture parameters can be classified into two groups depending on the dataset used to calculate them: field and feature parameters. While field parameters use all the height datasets, feature parameters only consider specific surface motifs.

Field parameters
Field parameters are derived from every point on the scale-limited surface. They can be classified according to the information they provide about the surface. The main subgroups are height, spatial, hybrid, functional , and related parameters, and fractal parameters.
| Parameter | Example units | Description | |
| Sa | μm | Density of peaks | |
| Sq | μm | Density of pits | |
| Ssk | unitless | Arithmetic mean peak curvature | |
| Height | Sku | unitless | Arithmetic mean pit curvature |
| Sp | μm | Five-point peak height | |
| Sv | μm | Five-point pit depth | |
| Sz | μm | Ten-point height | |
| Sal | μm | Mean hill local height | |
| Spatial | Str | unitless | Max. hill local height |
| Std | º | Std. dev. of hill local height | |
| Ssw | μm | Mean dale local depth | |
| Hybrid | Sdq | radians | Max. dale local depth |
| Sdr | % | Std. dev. of dale local depth | |
| Functional | |||
| Smr(c) | % | Mean hill area | |
| Smc(p) | μm | Max. hill area | |
| Sdc | μm | Std. dev. of hill area | |
| Areal for stratified surfaces | |||
| Sk | μm | Mean dale area | |
| Spk | μm | Max. dale area | |
| Spkx | μm | Std. dev. of dale area | |
| Svk | μm | Mean hill volume | |
| Svkx | μm | Max. hill volume | |
| Smrk1 | % | Std. dev. of hill volume | |
| Functional and related | Smrk2 | % | Mean dale volume |
| Sak1 | μm3/mm2 | Max. dale volume | |
| Sak2 | μm3/mm2 | Std. dev. of dale volume | |
| Areal material probability | |||
| Svq | μm | Hill count | |
| Spq | μm | Dale count | |
| Smq | % | Mean hill roundness | |
| Volume | |||
| Vvv | mm3/mm2 | Max. hill roundness | |
| Vvc | mm3/mm2 | Std. dev. of hill roundness | |
| Vmp | mm3/mm2 | Mean dale roundness | |
| Vmc | mm3/mm2 | Max. dale roundness | |
| Svsfc | unitless | Std. dev. of dale roundness | |
| Fractal | Sasfc | unitless | Mean hill form factor |
| Slsfc | unitless | Max. hill form factor | |
| Ssrc | unitless | Std. dev. of hill form factor | |
Feature parameters
Feature parameters provide detailed information about the individual characteristics of the surface. The motif’s size, shape, or area are some of the quantitative values that feature parameters offer.
| Parameter | Example units | Description | |
| Main feature parameters | Spd | 1/mm2 | Density of peaks |
| Svd | 1/mm2 | Density of pits | |
| Spc | 1/mm | Arithmetic mean peak curvature | |
| Svc | 1/mm | Arithmetic mean pit curvature | |
| S5p | μm | Five-point peak height | |
| S5v | μm | Five-point pit depth | |
| S10z | μm | Ten-point height | |
| Other feature parameters | Shh | μm | Mean hill local height |
| Shhx | μm | Max. hill local height | |
| Shhq | μm | Std. dev. of hill local height | |
| Sdd | μm | Mean dale local depth | |
| Sddx | μm | Max. dale local depth | |
| Sddq | μm | Std. dev. of dale local depth | |
| Sha | mm2 | Mean hill area | |
| Shax | mm2 | Max. hill area | |
| Shaq | mm2 | Std. dev. of hill area | |
| Sda | mm2 | Mean dale area | |
| Sdax | mm2 | Max. dale area | |
| Sdaq | mm2 | Std. dev. of dale area | |
| Shv | mm2 | Mean hill volume | |
| Shvx | mm3 | Max. hill volume | |
| Shvq | mm3 | Std. dev. of hill volume | |
| Sdv | mm3 | Mean dale volume | |
| Sdvx | mm3 | Max. dale volume | |
| Sdvq | mm3 | Std. dev. of dale volume | |
| Shn | mm3 | Hill count | |
| Sdn | unitless | Dale count | |
| Shape parameters | Shrn | unitless | Mean hill roundness |
| Shrnx | unitless | Max. hill roundness | |
| Shrnq | unitless | Std. dev. of hill roundness | |
| Sdrn | unitless | Mean dale roundness | |
| Sdrnx | unitless | Max. dale roundness | |
| vSdrnq | unitless | Std. dev. of dale roundness | |
| Shff | unitless | Mean hill form factor | |
| Shffx | unitless | Max. hill form factor | |
| Shffq | unitless | Std. dev. of hill form factor | |
| Sdff | unitless | Mean dale form factor | |
| Sdffx | unitless | Max. dale form factor | |
| Sdffq | unitless | Std. dev. of dale form factor | |
| Shed | unitless | Mean hill equivalent diameter | |
| Shedx | μm | Max. hill equivalent diameter | |
| Shedq | μm | Std. dev. of hill equivalent diameter | |
| Sded | μm | Mean dale equivalent diameter | |
| Sdedx | μm | Max. dale equivalent diameter | |
| Sdedq | μm | Std. dev. of dale equivalent diameter | |
| Shar | μm | Mean hill aspect ratio | |
| Sharx | unitless | Max. hill aspect ratio | |
| Sharq | unitless | Std. dev. of hill aspect ratio | |
| Sdar | unitless | Mean dale aspect ratio | |
| Sdarx | unitless | Max. dale aspect ratio | |
| Sdarq | unitless | Std. dev. of dale aspect ratio |
PARAMETER SELECTION
Which surface texture parameter should I use?
Choosing the correct surface texture parameter is crucial but can be challenging. Sa, for example, is widely used for its simplicity but may fail to capture the complexity of surfaces. Statistical analysis often identifies the most relevant parameters, particularly with large sample sets.
PARAMETER SELECTION
Which surface texture parameter should I use?
Choosing the correct surface texture parameter is crucial but can be challenging. Sa, for example, is widely used for its simplicity but may fail to capture the complexity of surfaces. Statistical analysis often identifies the most relevant parameters, particularly with large sample sets.

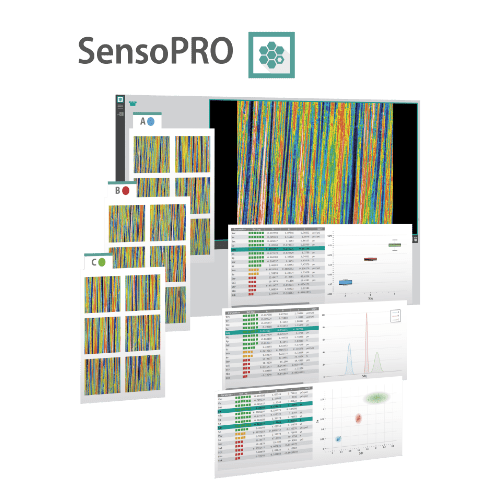
PARAMETER ANALYSIS
Optimizing surface parameter selection
Modern tools like Sensofar’s SensoPRO simplify parameter selection. By analyzing groups of samples, SensoPRO identifies key surface parameters, provides actionable insights, and sets tolerances, streamlining quality control and decision-making.
Modern tools like Sensofar’s SensoPRO simplify parameter selection. By analyzing groups of samples, SensoPRO identifies key surface parameters, provides actionable insights, and sets tolerances, streamlining quality control and decision-making.