Active Illumination Focus Variation
Carlos beschäftigt sich bei Sensofar seit 2010 mit der Entwicklung von Konfokal-, Interferometrie- und Fokusvariationstechnologien, seit 2018 hat er die Position des R&D Engineering Manager inne. Seine Interessen sind optomechanisches Systemdesign und Bildverarbeitung.
Fundierte Forschungsarbeit im Bereich der optischen Technik verleiht der Sensofar F&E-Gruppe eine herausragende Position, um in Bezug auf Innovation und höchstes technologisches Niveau immer auf dem neuesten Stand zu bleiben.
Active Illumination Focus Variation full article
Carlos Bermudez1, Pol Martinez1, Cristina Cadevall1, Roger Artigas1
1Sensofar-Tech, S.L. (Spain)
Proceedings Volume 11056, Optical Measurement Systems for Industrial Inspection XI; 110560W (2019)
Event: SPIE Optical Metrology, 2019, Munich, Germany
Abstract
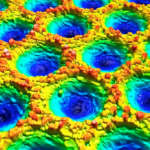
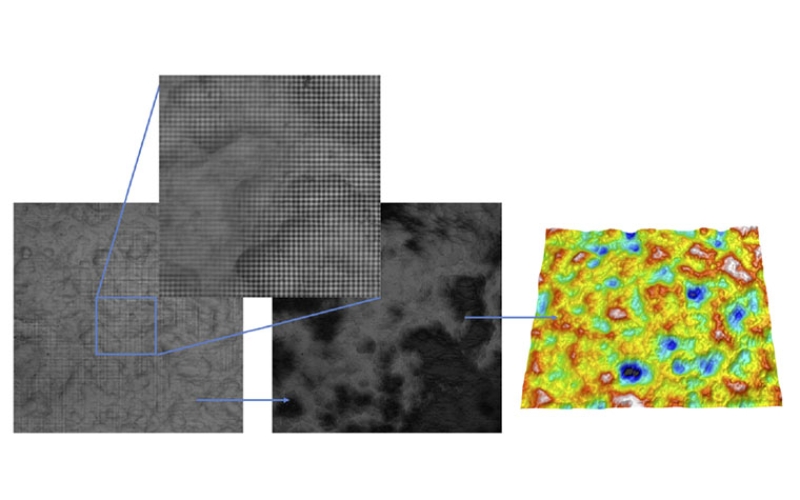
Focus Variation (FV) has been successfully employed for the three-dimensional measurement of rough surfaces. The technique relies on scanning the sample under inspection across the depth of focus of a high numerical aperture microscope objective, while computing the local contrast of its surface. Only those samples with sufficient texture will provide a usable axial response to compute its height location, limiting the application of Focus Variation to optically rough surfaces. Active illumination Focus Variation (AiFV) introduces an artificial texture on the field diaphragm position which is superimposed onto the surface. The benefit is a usable axial response, even when scanning an optically smooth surface, while minimizing the evaluation window of the focus operator close to the spatial autocorrelation length of the artificial texture.
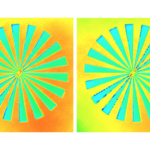
In this paper, we show the development of an Active illumination Focus Variation on an existing confocal microscope using Microdisplay Scanning technology. We analyzed the performance of AiFV on smooth surfaces with low frequency components, such as traceable Step Height or Type B2 roughness standards. Higher frequency samples such as random direction roughness standards or high-resolution targets are affected by the lateral resolution loss inherent on the AiFV technique. In this paper, we compare the lateral resolution limit of AiFV and Confocal Microscopy with the use of a Siemens Star specimen for a range of microscope objectives with numerical apertures from 0.3 to 0.95. Its influence on the computed ISO 25178 parameters on random surfaces is shown.